main menu
콘텐츠

 Smart Factory
Smart Factory  Smart Factory
Smart Factory Definition
A smart factory is a human-centered, advanced, intelligent factory that integrates all production processes, from product planning to sales, with ICT (Information and Communication Technology) to produce customized products at minimal cost and time.
- All manufacturing processes become smarter
-
 Planning and Design
Pre-production simulation in a virtual space Shortened production cycles, customized product development
Planning and Design
Pre-production simulation in a virtual space Shortened production cycles, customized product development -
 Production
Real-time information exchange between equipment, materials, and systems Mass production of a wide variety of products, improved energy-efficiency
Production
Real-time information exchange between equipment, materials, and systems Mass production of a wide variety of products, improved energy-efficiency -
 Distribution and Sales
Real-time automated order placement based on production status Reduced inventory costs, collaboration across all areas, including quality and logistics
Distribution and Sales
Real-time automated order placement based on production status Reduced inventory costs, collaboration across all areas, including quality and logistics
Scope of Application
Are changes to the production process alone enough to make a "smart factory"? No.
A smart factory encompasses all manufacturing processes, from product planning and development to mass production, from ordering to finished product shipment.
It encompasses all aspects of factory operations, from application systems to field automation and control automation.
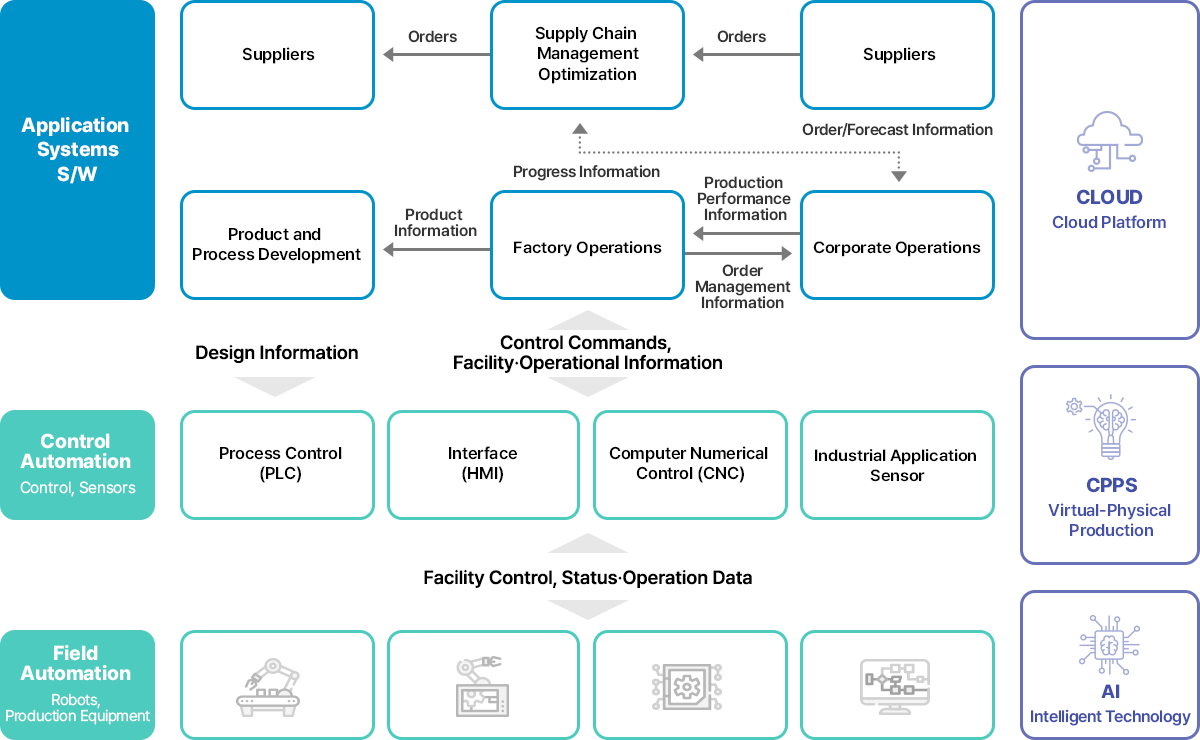 View Larger
View Larger
Smart Factory by Stage
Smart factories are categorized into "Building System Smartness Levels (Basic - Intermediate 1 - Intermediate 2 - Advanced)" based on the extent and capabilities of ICT technology utilization.
*Companies' comprehensive smart capabilities are measured and categorized into "Corporate Manufacturing Innovation Capability Levels (Level 1 ~ 5)".
Companies considering adopting a smart factory don't need to worry about achieving a high level from the beginning.
Smart factories can be implemented gradually depending on a company's capabilities and circumstances, so it's important to select and focus on the appropriate level and functions based on their circumstances.
Many small and medium-sized businesses are currently building basic systems that can be easily launched at relatively low cost, and are satisfied with the results that exceed expectations.
Even at this basic level, products manufactured can be aggregated and managed in real time, and even lot tracking is possible.
Wouldn't a smart factory of this level make a significant difference before and after its implementation?
A step-by-step implementation tailored to your business is possible.
| Div | Field Automation | Factory Operations | nterprise Resource Management | Product Development | Supply Chain Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced | IoT/IoS-based CPS | Business on the Internet CPS Network Collaboration |
|||
| IoT/IoS Integration | IoT/IoS(Modularization) Big Data-Based Diagnosis and Operation | ||||
| Intermediate 2 | Equipment Control Automation | Equipment Control Automation | Real-Time Factory Control | Simulation and Batch Process Automation | Multi-Product Development Collaboration |
| Intermediate 1 | Automatic Equipment Data Aggregation | Automatic Equipment Data Aggregation | Real-Time Decision Making | Automation and Collaboration of Technical Information Generation | Multi-Product Production Collaboration |
| Basic | erformance Aggregation Automation | Performance Aggregation Automation | Process Logistics Management (POP) | Server-Based Technology/Delivery Management | Dependence on a Single Parent Company |
| No ICT Application | Manual | Manual | Manual | Manual | Telephone and Email Collaboration |
Five Key Requirements
Below are five essential requirements for establishing and developing a smart factory at each level.
| Digitalization of 4M + 1E | The real-time digital values of each element of 4M + 1E (Man, Machinery, Material, Method, Environment) must be recognized, measurable information must be provided, and communication must be enabled. |
|---|---|
| Intellectualization | Solutions such as algorithms or artificial intelligence must be utilized to provide optimal or predictable solutions. |
| Integration Horizontal integration | which enables end-to-end information exchange through social networks and value chains, and vertical integration, from the lowest level of machinery to the corporate business level. |
| Creation of Engineering Knowledge | The ability to continuously acquire and store information and then gradually create manufacturing knowledge for automation must be built upon this information. |
| Connectivity with Smart Systems | The ability to connect with future smart products and communication standards must be established. |
※ Source : KOSMO Smart Factory Business Management System website.